Table of contents
- What is JWT Authentication?
- Step 1: Setting Up the Project
- Step 2: Getting the MongoDB Connection String
- Step 3: Creating a .env file
- Step 4: Set Up the Express app
- Step 5: Creating a User Model
- Step 6: Implementing Authentication Routes
- Step 7: Securing Routes with Middleware
- Step 8: Decode Details
- Step9: Testing the API
Authentication is an important part of web development. JSON Web Tokens (JWT) have become a popular method for implementing authentication in web applications due to their simplicity, security, and scalability. In this post, I'll guide you through implementing JWT authentication in a Node.js application using MongoDB for data storage.
Before starting, I’m assuming that you have Node.js, MongoDB, and VS Code installed on your machine and that you know how to create a MongoDB database and basic RESTful API.
If you haven’t yet, then you can check the following:
Let’s jump right into it!🚀
What is JWT Authentication?
JWT authentication relies on JSON Web Tokens to confirm the identity of users in a web app. A JSON Web Token is an encoded JSON object that is digitally signed using a secret key pair.
In simple words, JWT authentication is like having a secret passcode for a website. Once you're logged in, you get this passcode.
A JSON Web Token consists of three parts separated by dots (.):
Header
Payload
Signature
Here's the basic structure of a JWT:
xxxx.yyyy.zzzz
Header: This part has info about the token, like its type and how it's secured.
Payload: This part contains the claims that mean info about the user, like their username or role.
Signature: Ensures the integrity of the token and verifies that it hasn't been changed, which keeps the code safe from being messed with.
So, when you log in, you get this code. Every time you want to access something, you show this code to prove it's you. The system checks the code, sees it's valid, and lets you in!
Read more about JSON Web Token.
Now, let's see the steps of JWT authentication in your node.js project.
Step 1: Setting Up the Project
First, create a new directory for your project and navigate into it by using the following commands one by one.
mkdir nodejs-jwt-auth
cd nodejs-jwt-auth
Initialize the project by running the following command in the terminal (make sure you’re in your newly created project folder).
npm init -y
If you want more details about the above command, then you can click here.
Next, install the necessary dependencies by the following command:
npm install express mongoose jsonwebtoken dotenv
The above command will install
express: For building the web server.
mongoose: An ODM (Object Data Modeling) library for MongoDB.
jsonwebtoken: For generating and verifying JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for authentication.
dotenv: For loading environment variables from a
.envfile.
To this point, your package.json file should look like this:
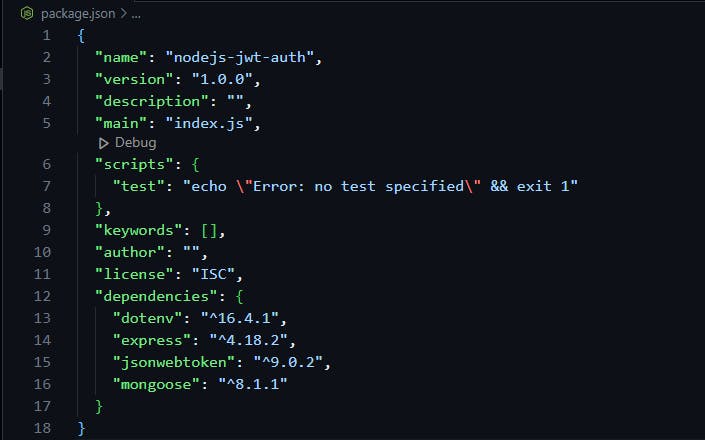
Step 2: Getting the MongoDB Connection String
To get the MongoDB connection string, check the following link. I've explained it step by step.
Getting the MongoDB Connection String
Step 3: Creating a .env file
To protect our MongoDB connection string, let’s create a new file named .env in the root directory.
Add the following code to the .env file.
MONGODB_URL=<Your MongoDB Connection String>
SECRET_KEY="your_secret_key_here"
Replace <Your MongoDB Connection String> with the connection string you obtained from MongoDB Atlas (in step 2) and your_secret_key_here with your desired secret message. Now your .env file should look like this.
MONGODB_URL='mongodb+srv://shefali:********@cluster0.sscvg.mongodb.net/nodejs-jwt-auth'
SECRET_KEY="ThisIsMySecretKey"
In the MONGODB_URL, at last, I’ve added nodejs-jwt-auth which is our database name.
Step 4: Set Up the Express app
Create a file named index.js in your root directory and add the following code to this file.
const express = require("express");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
require("dotenv").config(); //for using variables from .env file.
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
//middleware provided by Express to parse incoming JSON requests.
app.use(express.json());
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGODB_URL).then(() => {
console.log("MongoDB is connected!");
});
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello World!");
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is listening on port ${port}`);
});
Note: If you don't get how this above code is written, then you can check Build a RESTful API with Node.js, MongoDB, and Express. Over there I've explained it in detail.
Now, let's run the server by the following command.
node index.js
The output should be like the following image.
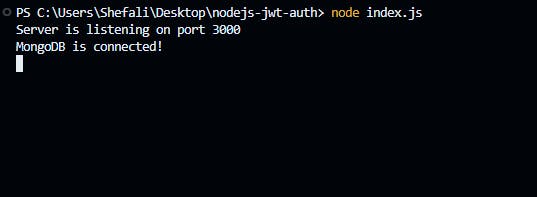
By using the command node index.js, you have to restart your server each time when you make changes to your file. To avoid this you can install nodemon using the following command.
npm install -g nodemon
Now run your server using the below command, it restarts the server automatically each time you make the changes to your file.
nodemon index.js
Step 5: Creating a User Model
Create a new directory named "models" in your root directory and inside it, create a new file named "User.js".
Now, let’s create a simple schema for our project. (Know more about Schemas)
Add the following code to the User.js file.
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
username: {
type: String,
required: true,
unique: true,
},
password: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("User", userSchema);
Step 6: Implementing Authentication Routes
Inside your root directory, create a new directory named "routes" and inside it, create a file named "auth.js".
Now, add the following code to this file:
const express = require("express");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const User = require("../models/User");
const router = express.Router();
// Signup route
router.post("/signup", async (req, res) => {
try {
const { username, password } = req.body;
const user = new User({ username, password });
await user.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "New user registered successfully" });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal server error" });
}
});
// Login route
router.post("/login", async (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
try {
const user = await User.findOne({ username });
if (!user) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: "Invalid username or password" });
}
if (user.password !== password) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Invalid username or password' });
}
// Generate JWT token
const token = jwt.sign(
{ id: user._id, username: user.username },
process.env.SECRET_KEY
);
res.json({ token });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal server error" });
}
});
module.exports = router;
Breaking down the above code:
Importing Dependencies:
const express = require("express");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const User = require("../models/User");
const router = express.Router();
Here, we are importing the following dependencies:
express: For building the web server.
jsonwebtoken: For generating and verifying JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for authentication.
User: Model imported from the
Usermodule, which we have created in step 5.router: The
Router()function from Express is used to define routes separately and then later combined into the main application.
Signup Route:
// Signup route
router.post("/signup", async (req, res) => {
try {
const { username, password } = req.body;
const user = new User({ username, password });
await user.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "New user registered successfully" });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal server error" });
}
});
This route listens for POST requests to
/signup.When a request is received, it extracts the
usernameandpasswordfrom the request body.It then creates a new instance of the
Usermodel with the providedusernameandpassword.The
save()method is called to save the new user to the database. (Learn about more Mongoose methods)If the user is successfully saved, it responds with a status code of 201 and a JSON message indicating "New user registered successfully".
If an error occurs during the process, it catches the error and responds with a status code of 500 and the error message "Internal Server Error".
Login Route:
// Login route
router.post("/login", async (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
try {
const user = await User.findOne({ username });
if (!user) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: "Invalid username or password" });
}
if (user.password !== password) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Invalid username or password' });
}
// Generate JWT token
const token = jwt.sign(
{ id: user._id, username: user.username },
process.env.SECRET_KEY
);
res.json({ token });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal server error" });
}
});
This route listens for POST requests to
/login.When a request is received, it extracts the
usernameandpasswordfrom the request body.It then searches for a user in the database with the provided
username.If no user is found, it responds with a status code of 401 (Unauthorized) and a JSON message indicating invalid username or password.
If a user is found, it checks if the provided
passwordmatches the stored password in the database.If the password does not match, it responds with a status code of 401 (Unauthorized) and a JSON message indicating invalid username or password.
If the password match, it generates a JWT using
jwt.sign()with the user's ID and username as the payload and a secret key.The generated token is then sent as a JSON response.
If there's an error during the process, it catches the error and responds with a status code of 500 and the error message "Internal Server Error".
Exporting Router:
module.exports = router;
Finally, the router is exported to be used in the index.js file.
Step 7: Securing Routes with Middleware
In the root directory, create a new file named middleware.js and add the following code to this file.
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
function verifyJWT(req, res, next) {
const token = req.headers["authorization"];
if (!token) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: "Access denied" });
}
jwt.verify(token, process.env.SECRET_KEY, (err, data) => {
if (err) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: "Failed to authenticate token" });
}
req.user = data;
next();
});
}
module.exports = verifyJWT;
This code is a middleware function for verifying JSON Web Tokens (JWT) in your application.
Breaking down the above code:
In the first line, we import the
jsonwebtokenlibrary.Then the
verifyJWTmiddleware function is defined, which takes three parameters:req(request object),res(response object), andnext(next middleware function).Inside the middleware function, it first extracts the token from the request headers.
If there's no token present in the request headers, it returns a 401 (Unauthorized) status along with a JSON response indicating "Access denied".
If a token is present, it tries to verify it using the
jwt.verify(). If verification fails, it catches the error and returns a 401 status with a JSON response indicating "Failed to authenticate token".If the token is successfully verified, it attaches the decoded token data to the
req.userobject.Finally, the
verifyJWTfunction is exported so that it can be used as middleware in other parts of the application.
Step 8: Decode Details
Now to decode the details, modify the index.js as follows:
const express = require('express');
const authRouter = require('./routes/auth');
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const verifyJWT = require("./middleware")
require("dotenv").config(); //for using variables from .env file.
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGODB_URL).then(() => {
console.log("MongoDB is connected!");
});
app.use(express.json());
//Authentication route
app.use('/auth', authRouter);
//decodeDetails Route
app.get('/decodeDetails', verifyJWT, (req, res) => {
const { username } = req.user;
res.json({ username });
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
In the above code,
app.use('/auth', authRouter);
The /auth route is handled by the authRouter, which contains endpoints for user authentication, such as login and signup.
app.get('/decodeDetails', verifyJWT, (req, res) => {
const { username } = req.user;
res.json({ username });
});
When a request is made to
/decodeDetails, theverifyJWTmiddleware verifies the JWT token attached to the request.If the token is valid, the middleware extracts the
usernamefrom the decoded token data stored inreq.user.Finally, the route handler sends a JSON response containing the
usernameextracted from the token.
Step9: Testing the API
For testing the API, I’m using the VS Code extension named Thunder Client.
Signup
Send a POST request to http://localhost:3000/auth/signup with Headers Content-Type : application/json and the following JSON body:
{
"username": "shefali",
"password": "12345678"
}
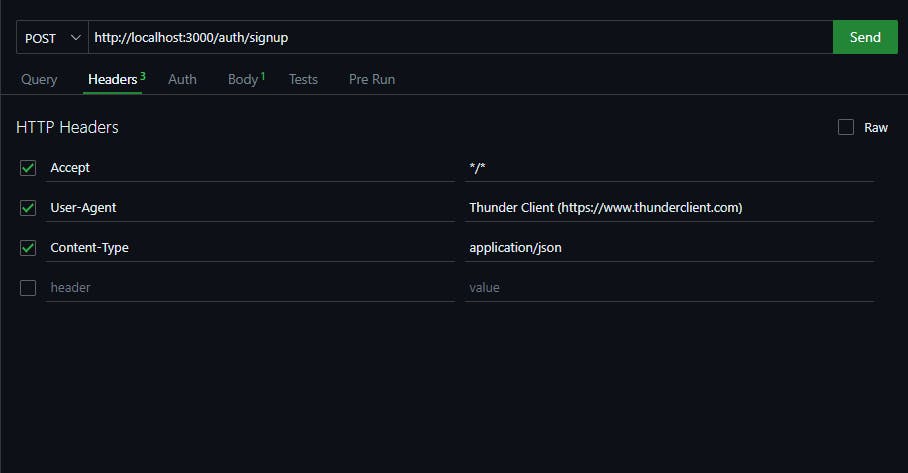
In the response, you'll see the message "New user registered successfully".
Login
Send a POST request to http://localhost:3000/auth/login with Headers Content-Type : application/json and the JSON body with the username and password, which you created in the signup route.
{
"username": "shefali",
"password": "12345678"
}
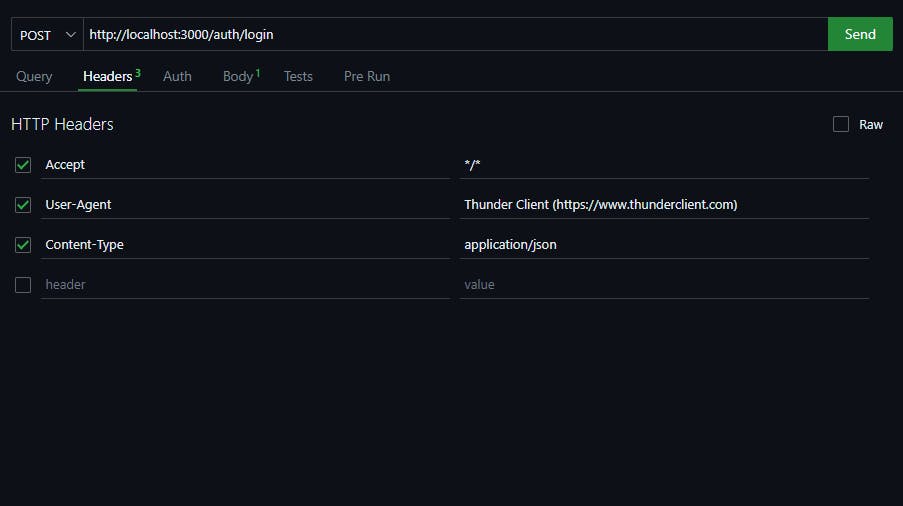
In the response, you'll receive a token. Note down this token as you'll need this while testing the decodeDetails route.
decodeDetails
Send a GET request to http://localhost:3000/decodeDetails with an Authorization header with the value of the token (You got it while testing the login route).
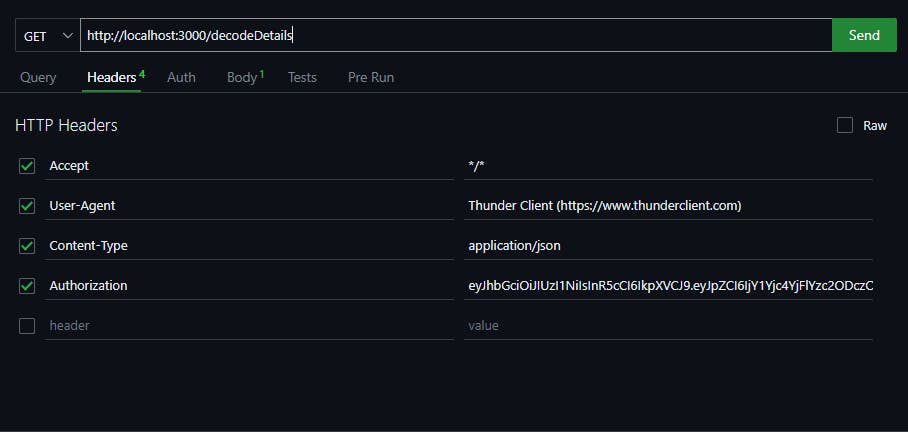
In the response, you'll get the username.
Congratulations! 🎉
You've successfully implemented JWT authentication in a Node.js application. This approach provides a secure and efficient way to authenticate users in your web applications.
That’s all for today.
I hope it was helpful.
Thanks for reading.
For more content like this, click here.
You can also follow me on X(Twitter) for getting daily tips on web development.
Keep Coding!!